iSAP partner with major Network vendors to deliver the need for low latency &high-performance network solutions.
If your business depends on the network to deliver mission-critical transactions, applications, and services, you do business with Cisco Networks.
Routers analyze the data being sent over a network, change how it is packaged, and send it to another network, or over a different type of network. They connect your business to the outside world, protect your information from security threats, and can even decide which computers get priority over others.
Depending on your business and your networking plans, you can choose from routers that include different capabilities. These can include networking basics such as
Firewall: Specialized software that examines incoming data and protects your business network against attacks
Virtual Private Network (VPN): A way to allow remote employees to safely access your network remotely
IP Phone network : Combine your company's computer and telephone network, using voice and conferencing technology, to simplify and unify your communications
Switches are used to connect multiple devices on the same network within a building or campus. For example, a switch can connect your computers, printers and servers, creating a network of shared resources. The switch, one aspect of your networking basics, would serve as a controller, allowing the various devices to share information and talk to each other. Through information sharing and resource allocation, switches save you money and increase productivity.
Ethernet Switches are broadly categorized into two main categories -- Modular and Fixed Configuration.
Modular Switches as the name implies, allows you to add expansion modules into the switches as needed, thereby delivering the best flexibility to address changing networks. Examples of expansion modules are application-specific (such as Firewall, Wireless, or Network Analysis), modules for additional interfaces, power supplies, or cooling fans. Cisco Catalyst 4K and 6K are good examples of Modular switches.
Fixed Configuration switches are switches with a fixed number of ports and are typically not expandable. This category is discussed in further detail below. Cisco Catalyst 2K, 3K and the Cisco300/500 series are good examples of Fixed Configuration switches. The Fixed configuration switch category is further broken down into
Unmanaged Switches
Smart Switches
Managed L2 and L3 Switches
Cisco has three layer hierarchical network model that consist of following layers
Core Layer
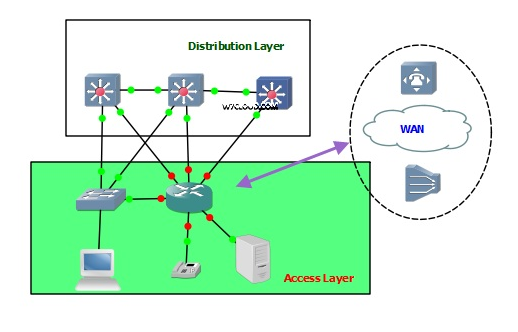
Distribution Layer
Access Layer
This three layered model is the basic foundation for creating small and larger Networks. Using this we can design a hierarchical network with dividing the network into 3 different layers which also help us in reducing the network complexity. Today's networks are complex and large, wide variety of technology, running multiple services and also having challenges with functionality, increasing demand of bandwidth and compatibility with other businesses and venders. So for designing large networks we need to have such hierarchical model for designing our network
Provide the flexibility in our network with three layers distribution, each layer is mapped with physical implementation and each of layers has its own features and functionality.
3 layer model is easier to understand and easy to grow your network.
3 layer model is easy to troubleshoot because of its logical distribution into layer, as each layer has its own functionality.
Allow us the lower cost in implementation.
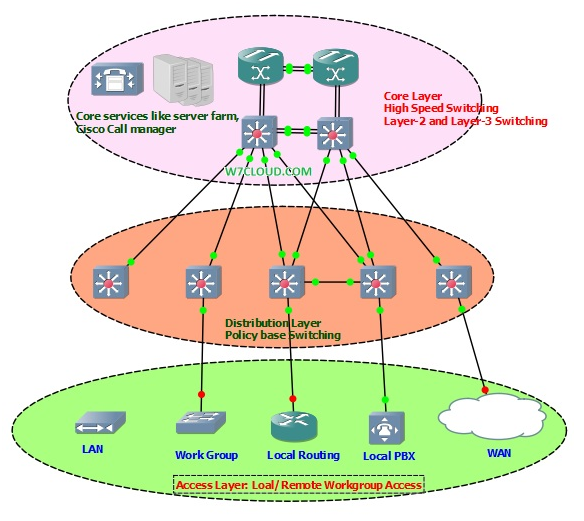
Core layer is the backbone layer of network running with high speed switching and transfers larger amount of data, also handle the requests of distribution layer. This layer has high Speed devices like high end routers and switches with large modules with layer-2 and layer-3 functionality.
Since core layer is the backbone of any network and providing services to other layers therefore this layer is reliable and have availability, also must be Redundant and have load balancing between its different links.
Cisco recommends that Core layer should have mesh topology and there should be no stuff like ACL, packet handling etc.
Some of key characteristics of core-layer are as following
Fast transport and large amount of data
Redundancy
High reliability and availability
Low latency and good manageability
Quality of service (QoS) classification, or other processes
Fault tolerance
Limited and consistent diameter
In a Network the number of router hops from edge to edge is called the diameter, it is considered good practice to design for a consistent diameter within a hierarchical network.
High end routers and switches
Layer-3 switches
Gateways and media converters
Soft Switches for IP telephone
The distribution layer is the isolation point between the network's access layer and core layers. Distribution layer is used for policy base services, normally having layer-2 switching devices.
Distribution layer control the access of data to core, provide the redundancy to access devices Route Redistribution, Route Filtering and router summarization are performed on Distribution layer. Distribution is normally a boundary between mediums in network. The distribution layer provides aggregation of routes providing route summarization to the core. In the campus LANs, the distribution layer provides routing between VLANs.
Some of key characteristics of distribution-layer are as following
Route filtering by source or destination address and filtering on input or output ports
Hiding internal network numbers by route filtering
Policy-based connectivity
Static routing
QoS mechanisms, such as priority-based queuing
Redundancy and load balancing
Aggregation of LAN wiring closets and WAN connections
Security filtering
Route summarization
Departmental or workgroup access
Broadcast or multicast domain definition
Routing between virtual LANs (VLAN)
Media translations (for example, between Ethernet and Token Ring)
Redistribution between routing domains (for example, RIP redistribution into OSPF)


Access layer is the lower layer of Cisco 3-layer model running different networks services and also responsible for providing access to different network resources. This is our local and remote workgroup-access that is providing access to different services like workgroups, WAN connectivity. Normally here we are running with low end devices like 2900 series switches. Access layer includes shared LAN, switched LAN and VLAN to workstations and servers, provide access to PSTN, WAN, DSL etc.
Different authentication servers like TACACS+, Radius are part of access layer. Access layer has running layer-2 switching also have layer-3 services for example router on stick for vlans, different type of protocols, QOS, packet filtering, route propagation are part of access-layer. You can implement features such as dial-on-demand routing (DDR) and static routing to control costs. Remote access can include virtual private network (VPN) technology.
Some of key characteristics of access-layer are as following
High availability
Layer 2 switching
Port security
Broadcast suppression
QoS classification and marking and trust boundaries
Rate limiting/policing
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) inspection
Virtual access control lists (VACL)
Spanning tree protocol (STP)
Trust classification
Power over Ethernet (PoE) and auxiliary VLANs for VoIP